11. Turtle Blocks Activity (TB)
The Sugar Graphical User Interface includes several Activities that can be used to learn how to program, known as programming environments. Some of them are Pippy, Etoys, Scratch and Turtle Blocks. The latter, Turtle Blocks Activity (Sugar Labs), is the one we'll use throughout this work. It is a development environment inspired in the LOGO programming language, created -among others- by the southafrican mathematician Seymour Papert in the decade of 1960; frequently identified with a turtle that drew on screen guided by programming that a user wrote, generally children and teenagers, as it was widely used to teach first steps in programming.
Initially called Turtle Art, (or Turtleart) this activity includes, among others, the ability to read voltages and resistances connected to the external microphone socket of the XO.
Toolbars of TB version 109
Activity toolbar (Project toolbar):

- Project Title
- Share button
- Save copy
Edit Toolbar:

- Copy
- Paste
Save Toolbar:
- Instant save
- Save as HTML
- Save as LOGO
- Save as Image
- Import from Journal
- Load Python block
- Load examples
View Toolbar:

- Fullscreen
- Cartesian coordinates
- Polar coordinates
- Centimeter coordinates
- Rescale coordinates
- Grow blocks
- Shrink blocks
Palette Toolbar:

- Turtle commands palette
- Pen commands palette
- Pen colors palette
- Numerical operators palette
- Flow operators palette
- Variable blocks palette
- Sensor palette
- Media object palette
- Additional options palette
- Presentation templates palette
- Trash bin
- Hide blocks
Help toolbar
 Enables contextual help
Enables contextual help CLEAN: Clean drawing in the canvas
CLEAN: Clean drawing in the canvas RUN: Runs the program (Start block) (maximum speed)
RUN: Runs the program (Start block) (maximum speed) RUN SLOWLY: Runs the program at low speed
RUN SLOWLY: Runs the program at low speed DEBUG: Runs the program block by block (to review the programming)
DEBUG: Runs the program block by block (to review the programming) STOP TURTLE: Stops the execution of the program (red: RUN / black: STOP)
STOP TURTLE: Stops the execution of the program (red: RUN / black: STOP) STOP: Closes Turtle Blocks Activity
STOP: Closes Turtle Blocks Activity
 HIDE BLOCKS: in this state, it shows blocks; when fill color is yellow, it hides them. You may toggle between views by clicking this icon found on the right of the "trash bin".
HIDE BLOCKS: in this state, it shows blocks; when fill color is yellow, it hides them. You may toggle between views by clicking this icon found on the right of the "trash bin".
Palettes
Turtle commands palette

Pen commands palette

Pen colors palette
Numerical operators palette
Flow operators palette
Variable blocks palette
Sensor palette
Media object palette
Additional options palette
Presentation templates palette
Trash bin
Help for each block in palettes (TB v.109)
We've included the help texts as they appear when invoked from inside the Activity: they consist of a brief description of the action that each block executes. An additional column with additional information has been included.
Turtle commands palette
| Block | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
forward |
Moves turtle forward | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate how much to move forward (by default: 100) |
back |
Moves turtle backward | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate how much to move backward (by default: 100) |
clean |
Clears the screen and reset the turtle | Erases the canvas, places the turtle at location (0,0), lowers the pen, selects red color, heading=0. It may be executed by clicking the eraser button (7th icon from main toolbar) |
left |
Turns turtle counterclockwise (angle in degrees) | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate how much to turn (by default: 90°) |
right |
Turns turtle clockwise (angle in degrees) | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate how much to turn (by default: 90°) |
arc |
Moves turtle along an arc | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate how much to turn (by default: 90°) as well as the desired radius (by default: 100) |
setxy |
Moves turtle to position xcor, ycor; (0, 0) is in the center of the screen | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the x coordinate (by default: 0) as well as the y coordinate (by default: 0) of the point on the screen you wish the turtle to be |
seth |
Sets the heading of the turtle (0 is towards the top of the screen.) | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the angle the turtle body will be looking at for moving forward (by default: 0) |
xcor |
Holds current x-coordinate value of the turtle (can be used in place of a number block) | - |
ycor |
Holds current y-coordinate value of the turtle (can be used in place of a number block) | - |
heading |
Holds current heading value of the turtle (can be used in place of a number block) | - |
Pen commands palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
penup |
Turtle will not draw when moved | - |
pendown |
Turtle will draw when moved | - |
setpensize |
Sets size of the line drawn by the turtle | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the numeric value for the line width (by default: 5) |
fillscreen |
Fills the background with (color, shade) | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the numeric value for the color (by default: 60) and shade (by default: 80). Resets turtle location to (0,0) |
pensize |
Holds current pen size (can be used in place of a number block) | - |
startfill |
Starts filled polygon (used with end fill block) | - |
stopfill |
Completes filled polygon (used with start fill block) | - |
Pen colors palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
setcolor |
Sets color of the line drawn by the turtle | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the numeric value for the color (by default: 0 red) |
setshade |
Sets shade of the line drawn by the turtle | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the numeric value for the shade (by default: 50) |
setgray |
Sets gray level of the line drawn by the turtle | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the numeric value for the gray level (by default: 100) |
color |
Holds current pen color (can be used in place of a number block) | - |
shade |
Holds current pen shade | - |
gray |
Holds current gray level | - |
red |
Red | 0 |
orange |
Orange | 10 |
yellow |
Yellow | 20 |
green |
Green | 40 |
cyan |
Cyan | 50 |
blue |
Blue | 70 |
purple |
Purple | 90 |
white |
White | -9998 |
black |
Black | -9999 |
Numerical operators palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
plus |
Adds two alphanumeric inputs | Can be used to concatenate text (character strings) |
minus |
Subtracts bottom numeric input from top numeric input | - |
product |
Multiplies two numeric inputs | - |
division |
Divides top numeric input (numerator) by bottom numeric input (denominator) | - |
identity ← |
identity operator used for extending blocks | It is a connector that can be extended to the right to avoid block overlap |
remainder |
modular (remainder) operator | Returns the remainder of the division of the top numeric input by the bottom numeric input |
sqrt |
calculates square root | - |
random |
returns random number between minimum (top) and maximum (bottom) values | Returns a random integer number. It has a min numerical block attached (by default: 0) and max (by default: 100) |
number |
used as numeric input in mathematic operators | In order to change the numeric value, all you need to do is to click within the block, delete the 100, and write a new value |
greater |
logical greater-than operator | - |
less |
logical less-than operator | - |
equal |
logical equal-to operator | - |
not |
logical NOT operator | - |
and |
logical AND operator | - |
or |
logical OR operator | - |
Flow operators palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
wait |
pauses program execution a specified number of seconds | It has a numerical block attached where you must indicate the time (by default: 1) |
forever |
loops forever | Repeats the programming block execution of the blocks connected to the lower/right side indefinitely or until the block "stop stack" is found |
repeat |
loops specified number of times | Repeats N times (by default: 4) the execution of the programming block that is connected its the lower/right side |
ifthen` |
if-then operator that uses boolean operators from Numbers palette | If the logical condition in the upper/right side is met, it executes the programming block to the lower/right side. Otherwise, execution continues with the one connected below |
if then else |
if-then-else operator that uses boolean operators from Numbers palette | If the logical condition in the upper/right side is met, the programming block connected to the bottom/center is executed. Otherwise, the one in the bottom/right side will be executed |
hspace |
jogs stack right | This is a connector that moves programming blocks to the right in order to avoid overlapping |
vspace |
jogs stack down | Same as above. Extensible by pushing "+" |
stop stack |
stops current action | - |
while |
do-while-True operator that uses boolean operators from Numbers palette | As long as the logical condition on the upper/right side is met ("if..."), it will execute the programming block connected to the bottom/right (after the "vertical spacer" block). It's useful to invoke it within a "named action" |
until |
do-until-True operator that uses boolean operators from Numbers palette | It executes the programming block that is connected to the lower/right (next to the "vertical spacer" block) until the logical condition in the upper/right side ("if...") is met. It's useful to invoke within a "named action" |
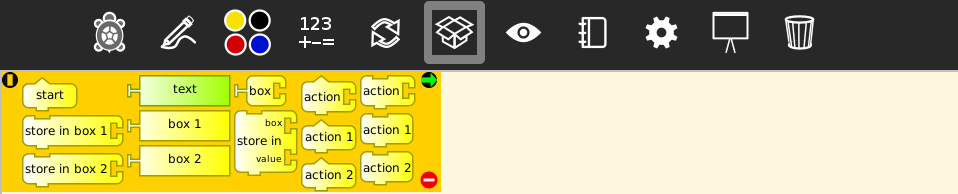
Variable blocks palette
The following blocks are used to define variables ("boxes") and subroutines ("actions"):
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
start |
connects action to toolbar run buttons | This block begins execution of the main programming code. Clicking it is the same as pushing the "RUN" button (rabbit) in the toolbar |
storeinbox1 |
stores numeric value in Variable 1 | For handling variables, following boxes have been added: "1", "2" and "named". It stores a numeric value, a string or a media object in "box 1" |
storeinbox2 |
stores numeric value in Variable 2 | idem. |
string |
string value | In order to change the numeric value, all you need to do is to click within the block, delete the 100, and write a new value |
box1 |
Variable 1 (numeric value) | Current contents of the variable called "box 1" |
box2 |
Variable 2 (numeric value) | Current contents of the variable called "box 2" |
box |
named variable (numeric value) | Current contents of the variable called "custom_name box" (by default: "my box") |
storein |
stores numeric value in named variable | Loads in the variable called "custom_name box" the numerical value, string or media object "value" (by default: "my box", 100) |
hat |
top of nameable action stack | Header for the programming block called custom_name (by default: "stack") |
hat1 |
top of Action 1 stack | Header for the programming block called "Action 1" |
hat2 |
top of Action 2 stack | Header for the programming block called "Action 2" |
| `stack | invokes named action stack | Invokes (for its execution) the programming block called "custom_name stack (by default: "action") |
stack1 |
invokes Action 1 stack | Invokes (for its execution) the programming block called action 1 |
stack2 |
invokes Action 2 stack | Invokes (for its execution) the programming block called action 2 |
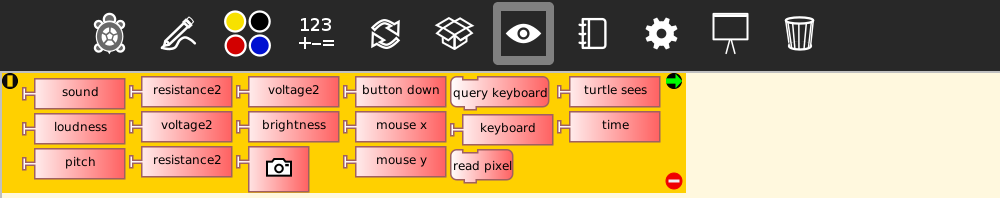
Sensor palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
kbinput |
query for keyboard input (results stored in keyboard block) | - |
keyboard |
holds results of query-keyboard block as ASCII | - |
readpixel |
RGB color under the turtle is pushed to the stack | The FILO stack ("First In - Last Out") holds values that can be retrieved in the inverse order that they are pushed. This pushes the RGB values that the turtle sees (Blue first, Red last) |
see |
returns the color that the turtle "sees" | - |
time |
elapsed time (in seconds) since program started | - |
lightsensor |
light level detected by light sensor | - |
camera |
camera output | - |
sound |
raw microphone input signal | Range -32000 to 32000 |
volume |
microphone input volume | Range 0 to 32000 |
pitch |
frequency for the most intense sound from microphone input | Resolution +/- 8 Hz |
resistance |
value for the resistance connected to the input microphone (measuring range: from 700 to 14000 ohm) | In case of using a stereo connector (TRS), it measures the resistance between the two TS contacts (tip and sleeve), corresponding to the left channel (CHL). Ranges: XO1: 750 Ω to 14 kΩ XO1.5: 2 kΩ to 420 MΩ XO1.75 SKU 206: 0 to 1x10^7 Ω |
voltage |
microphone input voltage | In case of using a stereo connector (TRS), it will measure the voltage between the TS contacts (tip and sleeve), corresponding to the left channel. Ranges: XO1: 0.4 to 1.85 V XO1.5: 0.17 to 3 V XO1.75 SKU 206: 0 to 3.03 V |
xyz |
push acceleration in x, y, z to the heap | The XO1.75 includes an accelerometer sensor. The results are pushed to the stack and may be retrieved with three "pop" blocks: one for the X component, another for the Y component and a third for the Z forward/backward component |
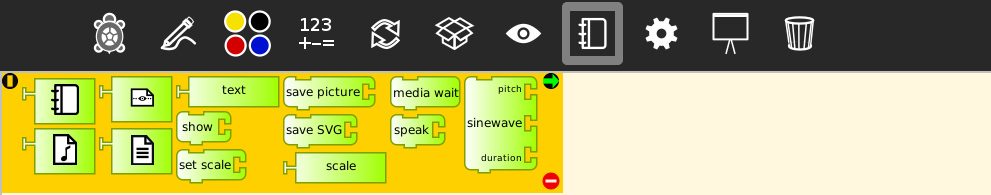
Media object palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
journal |
Sugar Journal media object | - |
audio |
Sugar Journal audio object | - |
video |
Sugar Journal video object | - |
description |
Sugar Journal description field | - |
string |
string value | - |
show |
draws text or show media from the Journal | It has a block attached that must be substituted for the object to be shown (by default: the string of value "text") |
setscale |
sets the scale of media | It has a block attached the desired scale must be specified (by default: 33) |
savepix |
saves a picture to the Sugar Journal | It has a block attached that indicates the name that the image will have (by default: "picture name"). It stores the image in *.png format |
savesvg |
saves turtle graphics as an SVG file in the Sugar Journal | It has a block attached that indicates the name that the image will have (by default: "picture name"). It stores the image in *.svg format |
scale |
holds current scale value | Full screen: 100 |
mediawait |
wait for current video or audio to complete | - |
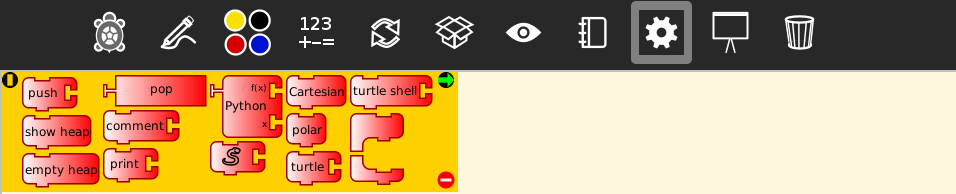
Aditional options palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
push |
pushes value onto FILO (first-in last-out heap) | - |
show heap |
show FILO in status block | - |
empty heap |
empty the FILO | - |
pop |
pop value off of the FILO (can be used in place of a number block) | - |
comment |
make a comment to your code | It is used to make the code more readable with the inclusion of comments and/or clarifications. (by default: comment block). The content of the comment is displayed in the status bar (bottom, center, with orange background) when the program is executed in "walk" or "debug" modes |
print |
print value in status block | A block or "status bar" is displayed in the bottom-center of the screen, with orange background. It can show numerical values, strings, or a combination of both by using the "+" block from the numerical operators palette |
Python |
a programmable block: used to add advanced single-variable math equations, e.g., sin(x) | Python function block: This block runs single Python statements or advanced mathematical calculations. By pushing the "+" it adds up to three variables (x, y, z) to the calculation to be done (by default: f(x)=x, x=100). E.g: Mathematics: sin(x) Time: time() |
userdefined |
runs code found in the tamyblock.py module found in the Journal | There are two applications: the first will run Python code that has been saved in the Journal with the name "myblock"; the second will execute the code loaded from "load Python block" from the third top icon (by default: 100). Growable block: accepts up to three parameters |
cartesian |
displays Cartesian coordinates | - |
polar |
displays Polar coordinates | - |
turtle |
chooses which turtle to command | It has a numerical block attached where the desired turtle must be specified (by default: 1) |
skin |
put a custom 'shell' on the turtle | - |
sandwichclamp |
top of a collapsible stack | - |
sandwichclamp(bottom) |
bottom of a collapsible stack | - |
Presentation templates palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
hide blocks |
declutters canvas by hiding blocks | - |
show blocks |
restores hidden blocks | - |
full screen |
hides the Sugar toolbars | - |
list |
presentation template: list of bullets | - |
journal 1x1a |
presentation template: select Journal object (no description) | - |
journal 1x1 |
presentation template: select Journal object (with description) | - |
journal 2x2 |
presentation template: select four Journal objects | - |
journal 2x1 |
presentation template: select two Journal objects | - |
journal 1x2 |
presentation template: select two Journal objects | - |
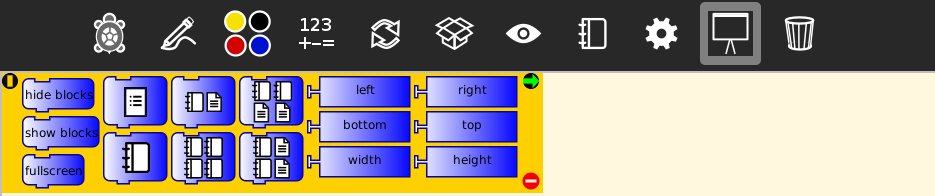
left |
xcor of left of screen | XO1: Returns value: -600 |
bottom |
ycor of bottom of screen | XO1: Returns value -600 |
width |
the canvas width | XO1: Returns value: 1200 |
right |
xcor of right of screen | XO1: Returns value: 600 |
top |
ycor of top of screen | XO1: Returns value: 450 |
height |
the canvas height | XO1: Returns value: 900 |
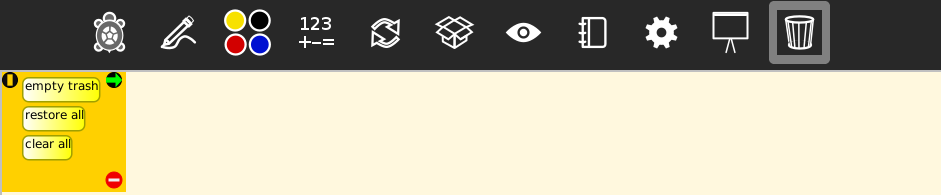
Trash bin
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
empty trash |
permanently deletes items in trash | - |
restore all |
restore all blocks from trash | - |
clear all |
move all blocks to trash | - |
Load Python Block
![]() Sometimes it may be necessary to execute a chunk of Python code in order to perform a specific task not supported within the TB blocks included in the Turtle Blocks Activity palettes. For this we can proceed in one of the following ways:
Sometimes it may be necessary to execute a chunk of Python code in order to perform a specific task not supported within the TB blocks included in the Turtle Blocks Activity palettes. For this we can proceed in one of the following ways:
- For users who know how to program in Python: Write the desired code in the Pippy Activity (for example) and save it in the Journal with the name "myblock". Then, within the TB program that is being written, include the Python block (from the additional options toolbar) and "load" it with the "myblock" name from the Sugar Journal.
- Often we wish to execute some of the actions included within the example "Python Blocks" (pysamples directory), such as "speak" (speak.py), emit a sound of a specific frequency (sinewave.py), etc. For this, we access the "SAVE toolbar", and within it, the icon "load Python Block" as the screenshot shows, and then select the desired block from the list.

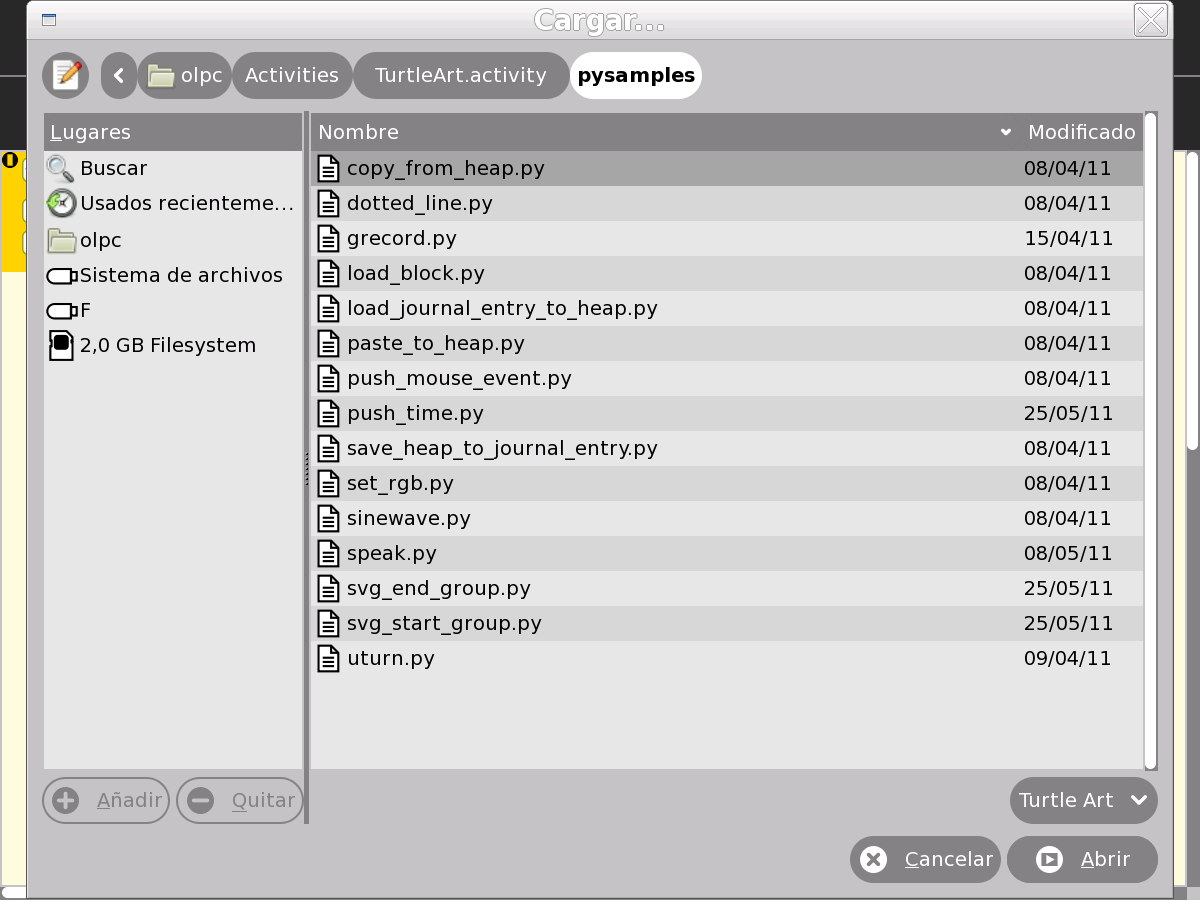
NOTE 1: The TB program that is written including a "Python Block" is not (generally speaking) an executable file; it implies that when copying it to another XO, before running it, you must "load" each Python block that is included since the copying process ignores these blocks (and therefore, does not execute them).
NOTE 2: When working with versions 130 and beyond, the example blocks speak.py (speak) and sinewave.py (emit sound) are included as TB blocks, so it's not necessary to proceed as described in item 2 above.
Blocks included in TB in version 130
The following tables include (only) the new blocks that were added in version 130 with respect to version 109. They appear in the Sensor blocks palette (known in version v.109 as "Sensor palette") and also in the Media blocks palette (known in v.109 as "Media object palette"). The original help text is included to give a brief description of the action they perform. We added a column that attempts to complete this information.
Sensor palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
mouse down |
returns 1 if mouse button is pressed | - |
mouse x |
returns mouse x coordinate | - |
mouse y |
returns mouse y coordinate | - |
resistance |
Value of the resistance connected to the microphone: (range 700 to 14000 ohms) | Measures the resistance between TS contacts (tip and sleeve, left stereo channel). The indicated range is only correct for the XO1. Ranges: XO1: 750 Ω to 14 kΩ XO1.5: 2kΩ to 420 MΩ XO1.75 SKU 206: 0 to 1x10^7 Ω |
resistance2 |
Value of the resistance connected to the microphone: (range 700 to 14000 ohms) | Measures the resistance between RS contacts (ring and sleeve, right stereo channel). The indicated range is not correct. Ranges: XO1: 750 Ω to 14 kΩ XO1.5: 2kΩ to 420 MΩ XO1.75 SKU 206: 0 to 1x10^7 Ω |
voltage |
DC value of voltage connected to the microphone input (range: 0.40 to 1.90 V) | In case of using a stereo connector (TRS), it measures the voltage between the TS contacts (tip and sleeve), corresponding to the left channel. The indicated range corresponds only with XO1. Ranges: XO1: 0.4 to 1.85 V XO1.5: 0.17 to 3.0 V XO1.75 SKU 206: 0 to 3.03 V |
voltage2 |
DC value of voltage connected to the microphone input (range: 0.40 to 1.90 V) | In case of using a stereo connector (TRS), it measures the voltage between the RS contacts (ring and sleeve), corresponding to the right stereo channel. The indicated range is incorrect. Ranges: XO1: 0.4 to 1.85 V XO1.5: 0.17 to 3.0 V XO1.75 SKU 206: 0 to 3.03 V |
Media blocks palette
| Blocks | Help (original) | Additional clarification |
|---|---|---|
speak |
Emits thru the speakers (as synthesized voice) the phrase contained in the text block to to the right | It includes a block that indicates the text to be synthesized (by default: hello). Numerical values can be included |
sinewave |
Plays a sinewave at frequency, amplitude, and duration (in seconds) | For generating sounds through the speakers or the headphone output. Amplitude is in arbitrary units (by default: frequency: 1000 Hz, amplitude: 5000 and duration: 1s) |